Circular Economy:
A Guarantee for Sustainable Production and Business Success
"Made in Germany" – an outdated model? Foreign low-cost competitors are putting significant pressure on German industry. To counteract this downward trend and remain competitive globally, manufacturers should look to new business opportunities within the circular economy.
For decades, the “Made in Germany” label has provided companies with considerable advantages in international markets. German-made products were known for their high quality and durability, which often gave them a competitive edge over foreign counterparts despite higher prices.
In today’s fast-paced world, however, it’s precisely this durability that can be a disadvantage for German products. Household appliances, washing machines, or cars, for instance, are rarely used until they stop functioning. Consumers are partly responsible, but regulatory requirements for energy efficiency, safety, and fire protection also often demand early replacement.
This trend has far-reaching implications for German industry: if products no longer need to be highly durable, top-tier quality becomes less critical. To keep up with low-cost products from abroad, German companies would need to produce more affordably – which is hardly feasible under current conditions. Overbearing bureaucracy, high energy and labor costs, and the skilled labor shortage present almost insurmountable challenges for German industry. According to a recent ifo survey, nearly all sectors see their competitiveness at risk.
What are the Core Principles of a Circular Economy with Sustainable Production?
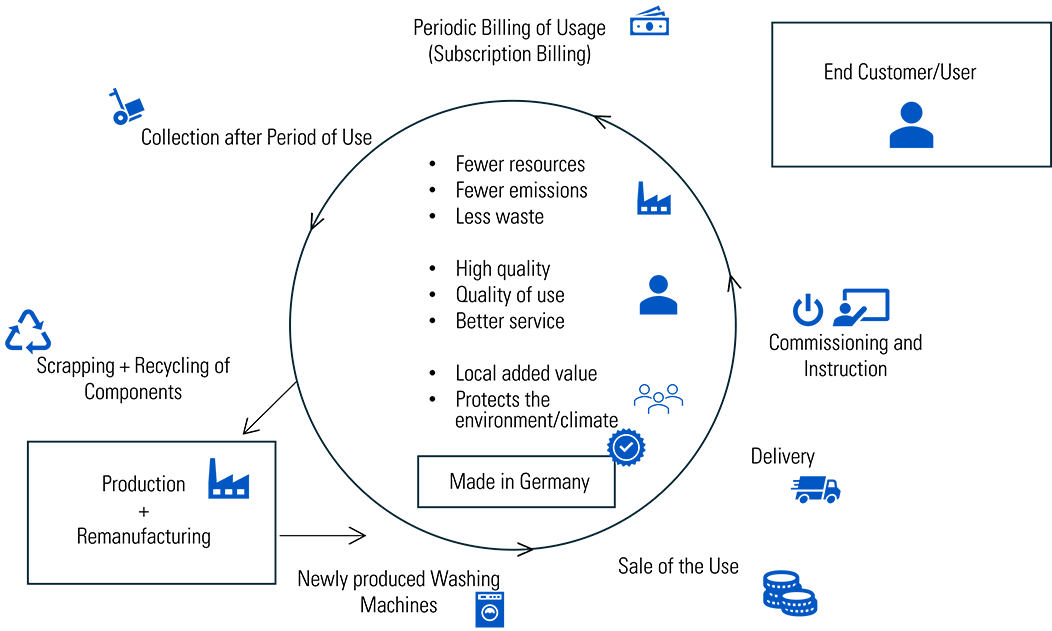
One opportunity to escape this downward spiral is to shift production towards a circular economy. Companies that manufacture sustainably and resource-efficiently can once again leverage the “Made in Germany” label and tap into new business potential.
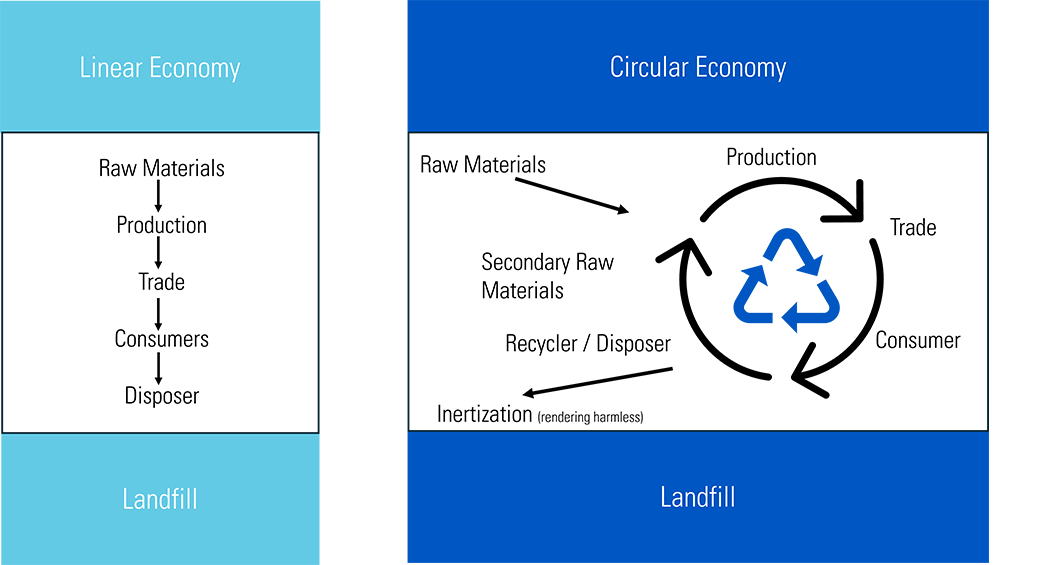
A circular economy is a regenerative system aimed at maximizing resource efficiency while minimizing waste, emissions, and energy usage. To ensure long-lasting material and product life cycles, items should ideally be reused or recycled, with recycling as a secondary option.
In contrast, the traditional linear economy, often called a “throwaway economy,” involves discarding or incinerating a large portion of raw materials when a product is no longer used; only a small percentage is recycled.
![[Translate to Englisch:] [Translate to Englisch:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/8/a/csm_kreislaufwirtschaft-bild_da07b4c96d.jpg)